Generative AI Explained: How ChatGPT and Similar Tools Actually Work
Published by The Consultancy World | AI Strategy Experts | Last Updated: December 2025
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that create new content - text, images, code, audio, or video - rather than simply analysing or classifying existing data. Unlike traditional AI that recognises patterns or makes predictions, generative AI produces original outputs based on learned patterns from vast training datasets. Systems like ChatGPT, Claude, Midjourney, and GitHub Copilot have revolutionised business operations by democratising content creation, automating complex writing tasks and enabling sophisticated human-AI collaboration. Understanding how these tools work enables business leaders to leverage their capabilities effectively whilst recognising their limitations and managing associated risks.
This guide demystifies generative AI technology and explains its practical implications for business operations.
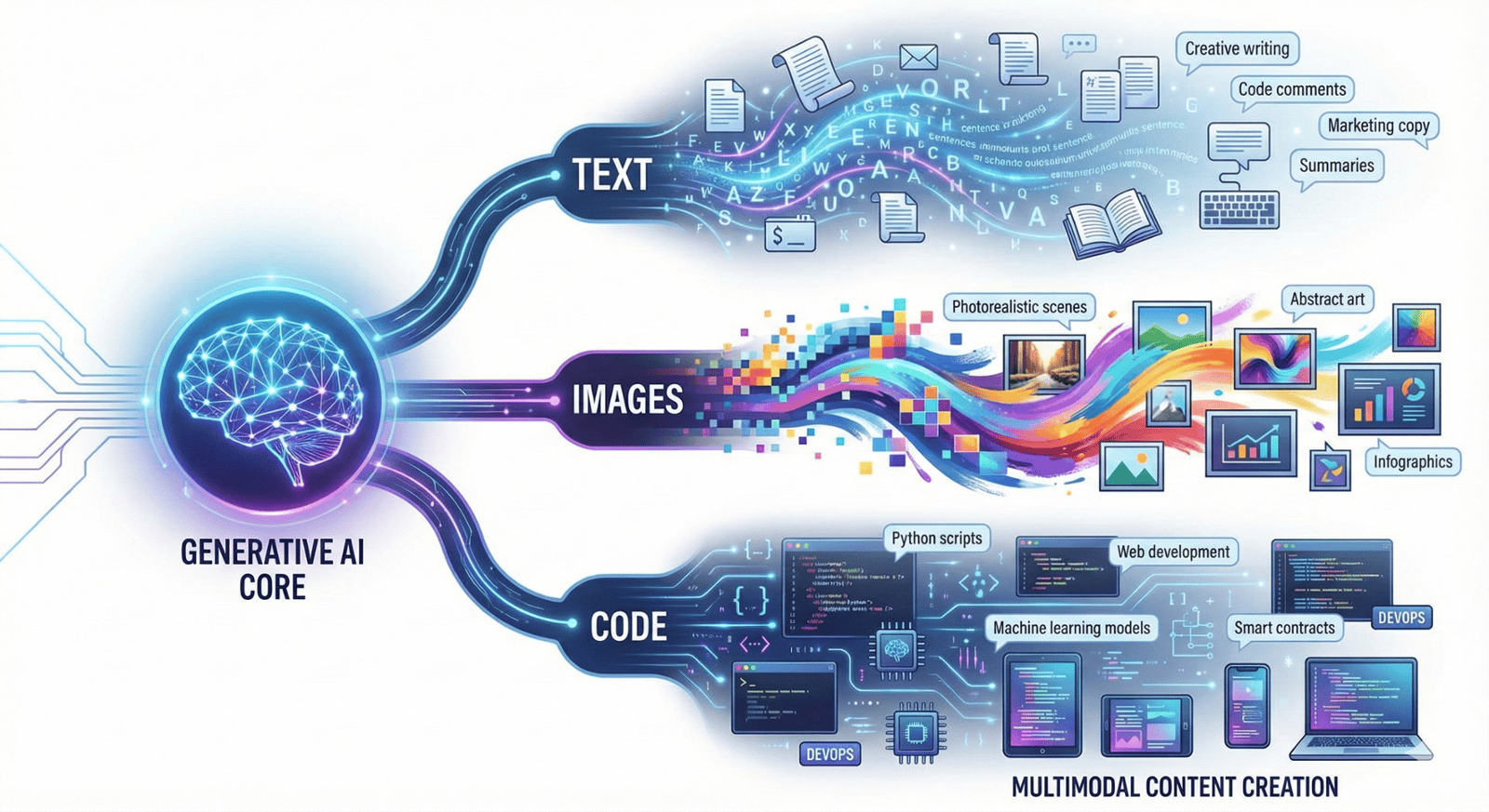
What Is Generative AI? The Core Concept
Traditional AI vs Generative AI
Traditional AI (Analysis and Classification):
• Takes input and provides assessment: "Is this email spam?"
• Makes predictions: "This customer will likely churn"
• Recognises patterns: "This image contains a cat"
• Classifies information: "Route this enquiry to technical support"
Generative AI (Creation and Synthesis):
• Creates new content based on prompts: "Write a professional email explaining our refund policy"
• Generates images from descriptions: "Create a logo for a technology consultancy"
• Produces code from requirements: "Write a Python function to calculate compound interest"
• Synthesises information: "Summarise these three research reports into key findings"
The Fundamental Difference: Traditional AI analyses what exists. Generative AI creates what doesn't yet exist.
How ChatGPT and Similar Tools Actually Work
The Foundation: Large Language Models (LLMs)
Generative AI text tools like ChatGPT, Claude and Bard are powered by Large Language Models - massive AI systems trained on enormous text datasets (books, websites, articles, code) containing billions to trillions of words.
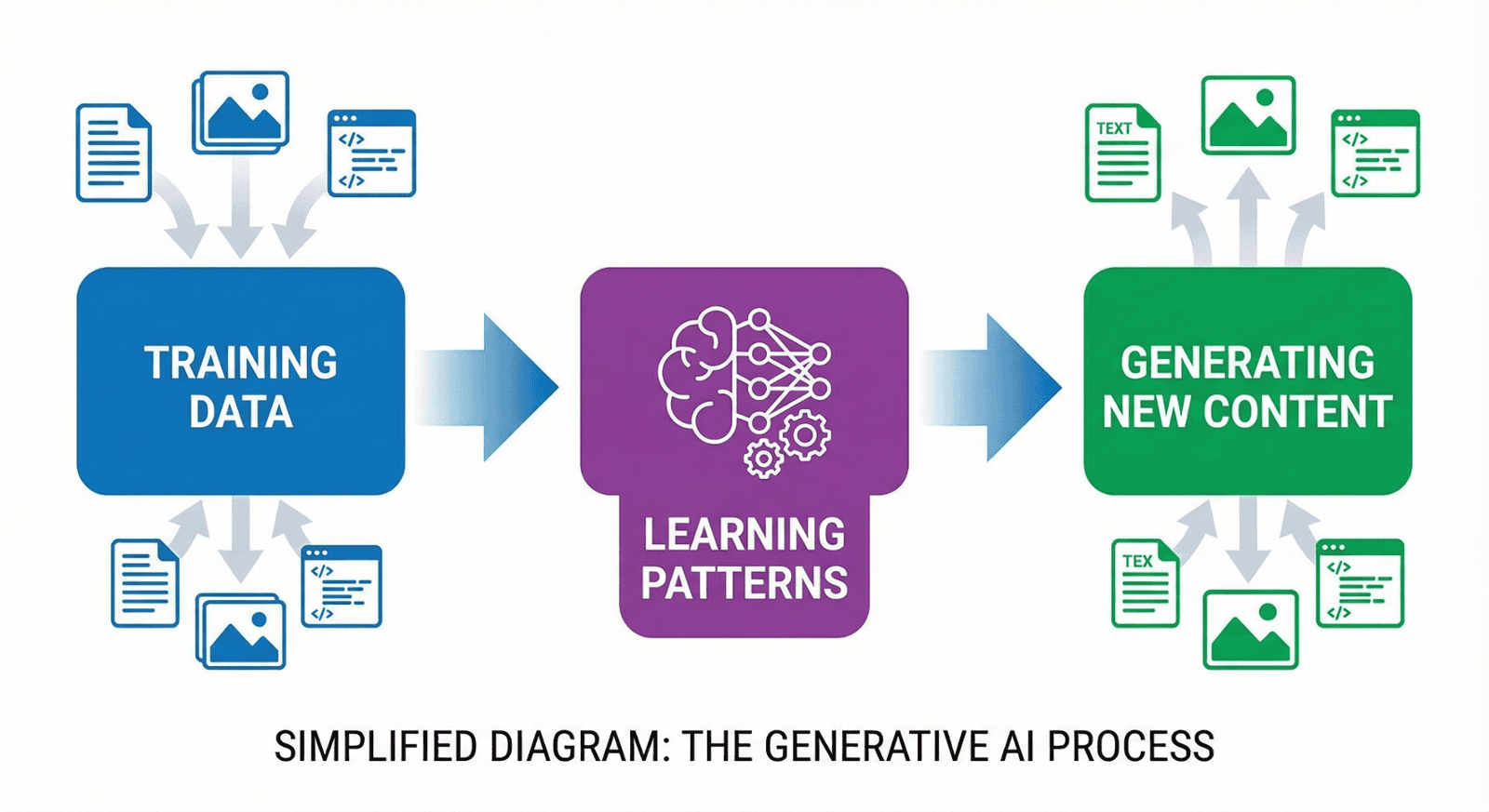
The Training Process Explained Simply
Step 1: Learning Language Patterns (Pre-Training)
The model reads billions of sentences and learns:
• Which words typically follow other words
• How sentences are structured
• What makes text coherent and meaningful
• Relationships between concepts
• Patterns in how information is expressed
Think of it like a musician who has listened to thousands of songs and learned chord progressions, melody structures, and musical patterns—not by memorising specific songs, but by understanding the principles of music composition.
Step 2: Learning to Follow Instructions (Fine-Tuning)
The model is then trained on examples of following instructions:
• Question-answer pairs
• Task completion examples
• Conversations demonstrating helpfulness
• Feedback from human reviewers
This teaches the model to be useful, accurate, and aligned with user intentions.
Step 3: Generating Responses
When you type a prompt, the model:
1. Analyses your request, understanding context and intent
2. Generates responses word-by-word, predicting what should come next based on all its training
3. Produces text that is statistically likely to be relevant, coherent, and helpful
Critical Insight: The model isn't searching a database for pre-written answers. It's generating responses in real-time based on patterns learned from its training data—similar to how humans generate speech based on language patterns we've internalised.
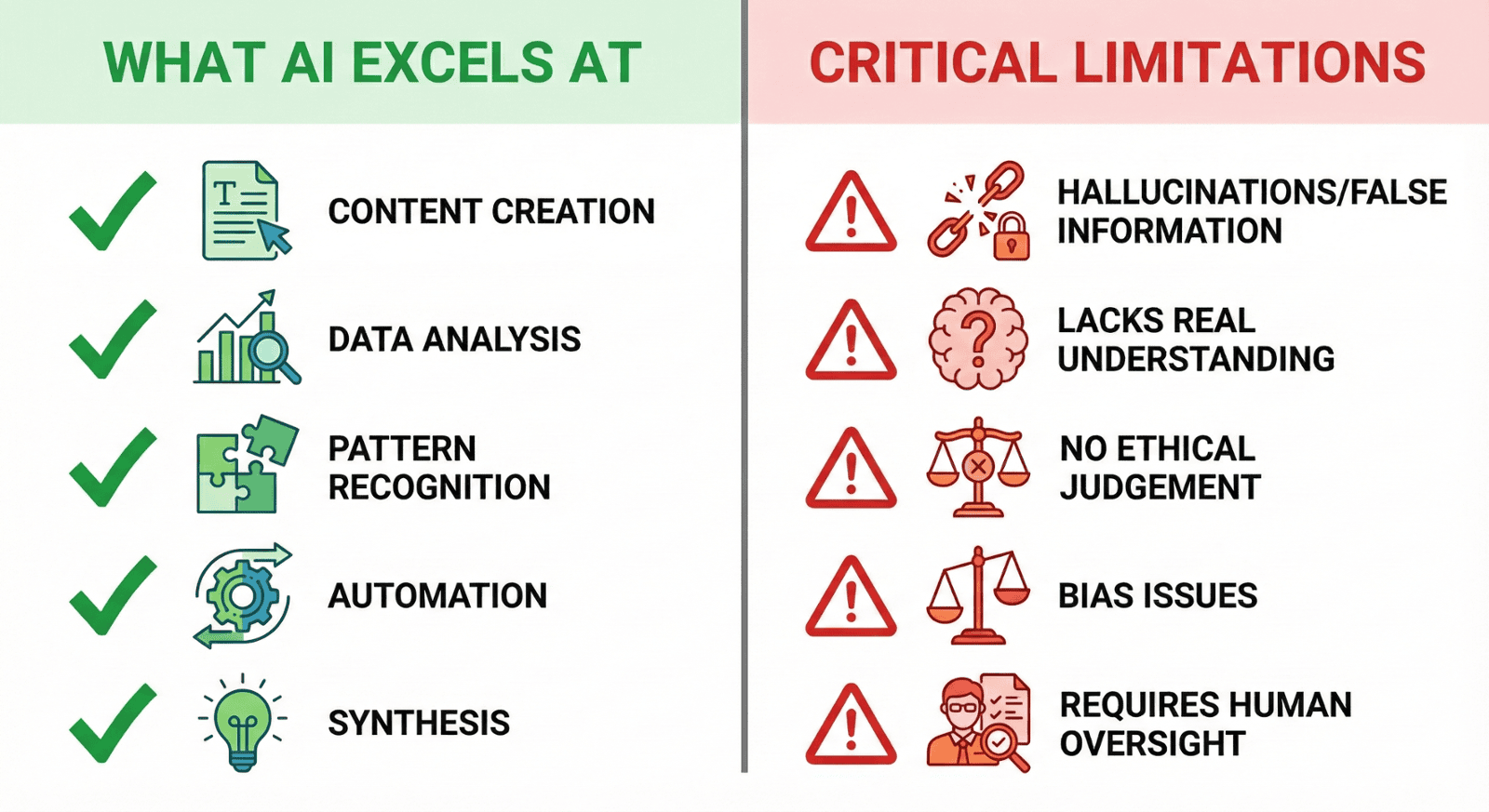
What Generative AI Can and Cannot Do
What These Systems Excel At:
1. Content Generation and Writing
• Professional emails, reports, and proposals
• Marketing copy and social media content
• First drafts of articles and blog posts
• Meeting notes and summaries
• Standard business correspondence
Quality Level: Good to excellent for first drafts; requires human review and refinement
2. Information Synthesis and Summarisation
• Condensing long documents into key points
• Comparing multiple sources
• Explaining complex topics simply
• Answering questions based on provided information
Quality Level: Excellent when working with provided content; may be inaccurate when relying purely on training knowledge
3. Code Generation and Technical Tasks
• Writing functions and scripts
• Debugging existing code
• Explaining technical concepts
• Creating formulas and calculations
Quality Level: Very good for common programming tasks; requires verification for production use
4. Creative Brainstorming and Ideation
• Generating options and alternatives
• Exploring different approaches
• Creating variations on themes
• Suggesting names, titles, and concepts
Quality Level: Excellent for expanding possibilities; human judgement required for final selection
5. Data Structuring and Formatting
• Converting unstructured text to structured formats
• Creating tables and summaries
• Organising information logically
• Reformatting content
Quality Level: Excellent for most formatting tasks
Critical Limitations Business Leaders Must Understand:
1. Hallucinations (Confident Fabrication)
Generative AI sometimes produces plausible-sounding but entirely fabricated information—citing non-existent studies, inventing statistics, or creating false facts with complete confidence.
Business Risk: Legal exposure, reputation damage, incorrect decision-making
Mitigation: Never use AI output without human verification, especially for facts, citations, or technical specifications
2. No Real-Time Knowledge
Models don't know current events, recent news, or information published after their training cutoff unless specifically designed with web search capabilities.
Business Risk: Outdated recommendations, incorrect current information
Mitigation: Verify time-sensitive information independently
3. Lack of True Understanding
These systems process statistical patterns but don't "understand" in the human sense. They can produce text that sounds intelligent without genuine comprehension.
Business Risk: Missing context, inappropriate responses in nuanced situations
Mitigation: Human oversight for consequential decisions
4. Bias and Inconsistency
AI systems reflect biases present in training data and can produce different outputs for similar prompts.
Business Risk: Discrimination, inconsistent customer service, inappropriate content
Mitigation: Regular auditing, diverse testing, clear guidelines
5. No Judgement or Ethics
AI systems don't have moral judgement, values, or understanding of business context beyond patterns in training data.
Business Risk: Inappropriate suggestions, missing ethical considerations
Mitigation: Human decision-making on strategic, ethical, or sensitive matters
Want to Leverage Generative AI Effectively While Avoiding Costly Mistakes?
Understanding how generative AI works is just the beginning. The real challenge is implementing these tools strategically within your organisation—knowing:
• Which business processes benefit most from generative AI
• How to integrate AI tools with existing workflows
• What governance and quality control measures you need
• How to train teams for effective AI utilisation
• What risks to mitigate and how
This is where businesses need expert strategic guidance, not just technology access.
The Consultancy World Specialises In Practical Generative AI Strategy
We help businesses move beyond experimentation to systematic, effective AI integration that delivers measurable ROI whilst managing risks appropriately.
In a complimentary consultation, we'll:
✓ Identify your highest-value generative AI opportunities
✓ Assess your readiness and risk profile
✓ Recommend specific tools and implementation approaches
✓ Provide a practical roadmap for strategic deployment
✓ Address your concerns about quality control and governance
[Schedule Your Free Generative AI Strategy Session →](https://www.theconsultancy.world/book-call)
No sales pressure. Just actionable insights from experienced AI strategists.
Conclusion: The Generative AI Revolution Is Here
Generative AI represents the most significant democratisation of AI capabilities in business history. For the first time, organisations of any size can leverage sophisticated AI to automate content creation, enhance productivity, and compete with larger competitors.
However, effective implementation requires understanding both capabilities and limitations. The most successful organisations approach generative AI strategically - with clear use cases, appropriate governance, realistic expectations and expert guidance.
The technology is accessible. Strategic implementation separates winners from those who waste investment on disappointing results.
This article was written by The Consultancy World's expert team and reflects current best practices in AI strategy as of December 2025.
Last Updated: December 18, 2025
Reading Time: 12-15 minutes
Level: Beginner to Intermediate
Audience: Business Leaders, Marketing Directors, Operations Managers
© 2025 The Consultancy for Business Solutions Ltd. All rights reserved.
